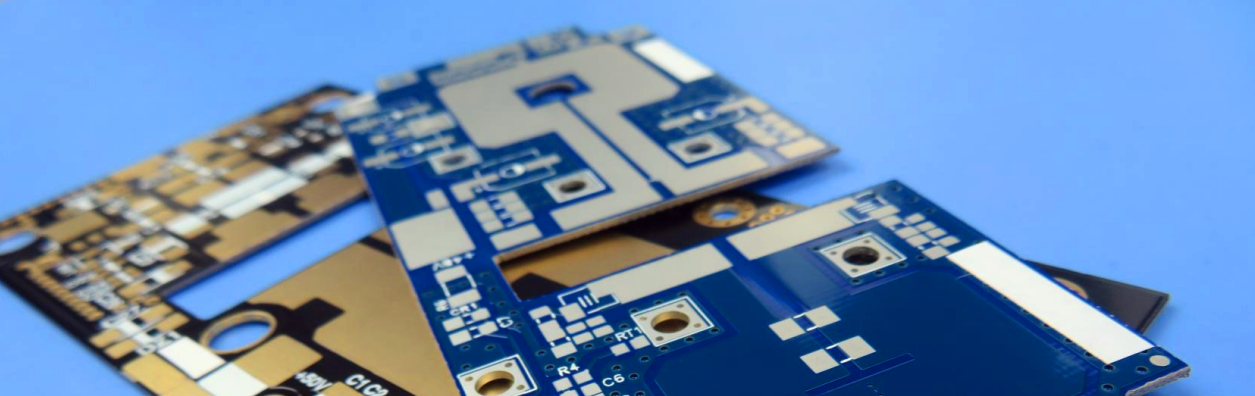
1. Printed Circuit Board (FPC)
The FPC is made up of a plastic film, copper foil, and a binding agent. The FPC can contain circuits in multiple layers and support chip mounting or chip surface mounting, in addition to being bendable and flexible, ultrathin, and high-precision (SMT). The FPC is also known as the flex circuit, flexible PCB, membrane, flexible electronics, Large Fine Line FPC PCB, and so on.
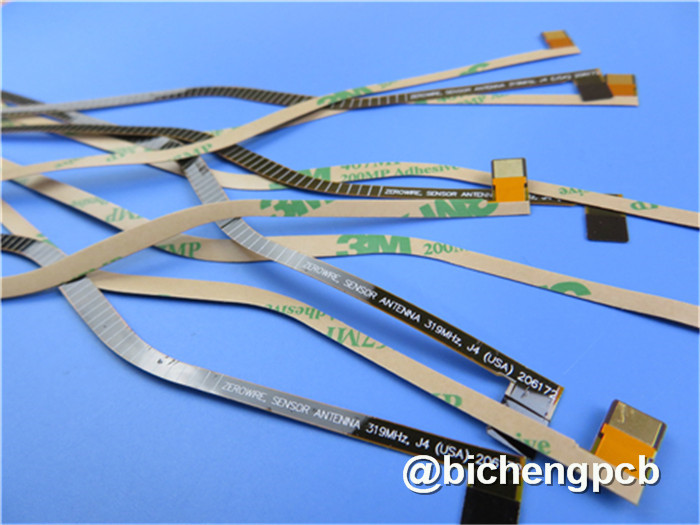

As with other substrates, higher wire density and more layers are required for the FPC to improve performance while lowering power consumption in signal transmission. FPC's technology threshold is higher due to the complexity of its manufacturing process.
Application
The FPC is widely used in a variety of products, almost all of which are high-tech. It is most commonly found in communication devices such as smartphones. Over 40% of the PCBs in a smartphone are FPCs. In addition, the FPC is used in laptops, autotronics, medical devices, weapons, and wearables. The miniaturization trend of products increases the importance of the FPC. According to statistics, the iPhone X uses approximately 20 FPCs. In addition to the iPhone, the FPC is frequently used in other terminal devices, such as the antenna FPC, backlight module FPC, camera lens FPC, touch screen FPC, Touch ID FPC, SIM FPC, laptop screen connection FPC, car image sensor FPC, car light assembly FPC, and so on. As a result, the significance of FPC is demonstrated.
Texture
The
Flxible PCB can be classified according to material into the PI, MPI, and LCP. Because the performance of PI is so low that it is almost phased out, the MPI is a modified PI. Currently, the two most common FPC materials are MPI and LCP. Because the LCP performs better, its price is significantly higher. In terms of price-to-performance ratio (PPR), the MPI is generally thought to have a higher PPR. The MPI, in particular, has become a threat to the LCP after significant improvements in recent years. In 2018, Apple, for example, decided to replace LCP FPCs with MPI FPCs in order to reduce costs. The primary consideration in the selection of FPC materials is power consumption in signal transmission. Although there is no significant difference in power consumption in low-frequency transmission, as the frequency increases, the power consumption of the PI gradually increases, as does that of the MPI and LPC. As a result, the LCP has a greater advantage in high-frequency transmission. As a result, because a portion of the signal transmission frequency in 5G will exceed 24GHz, the FPC requirements will be higher.
2. Rigid-Flex Printed Circuit Board (RFPCB)
The RFPCB is an abbreviation for Radio Frequency Power Control Board. In general, an RFPCB is formed when an FPC is laminated between two RFPCBs to form a complete PCB. The integration of HDI technology and the trend of high-frequency signal development will increase the popularity of the RFPCB.
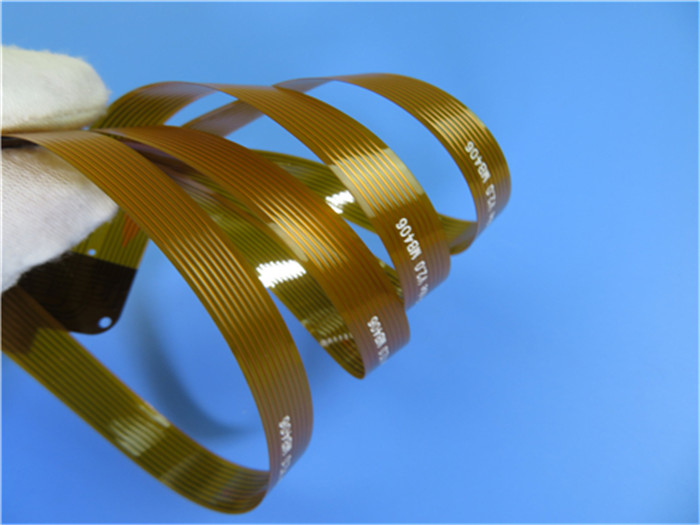

Traditionally, the FPC and
Rigid-Flex PCB FR-4 Poyimide are linked together using a connector or hot bar. To effectively improve reliability, the RPCB transmits signals through RPCB FPCRPCB to shorten the distance and increase the speed of signal transmission.
Furthermore, this can save space on the PCB and the connector or hot bar process, making product assembly easier. Although RPCB is more expensive, it can be used extensively and is customizable.
The RPCB is frequently used in the aerospace, medical, and arms industries due to its high reliability. RPCBs are commonly found in smartphones, PV panels, battery packs, wearables, and advanced storage devices.
 Call Us Now !
Tel : +86 755 27374946
Call Us Now !
Tel : +86 755 27374946
 Order Online Now !
Email : info@bichengpcb.com
Order Online Now !
Email : info@bichengpcb.com