Rigid PCB vs. Rigid Flex PCB vs. Flex PCB Comparison
The majority of electronic equipment contains printed circuit boards, also known as PCBs. The boards physically and mechanically support the device while also connecting the electronic components.
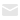
PCBs are typically constructed from non-substrate materials with copper circuitry layers. Rigid PCB, Flex PCB, and, last but not least, a hybrid of both Rigid-Flex PCB are the three major types of PCBs.
Although all electronic devices use some form of PCB to function, most people are unaware of which one is used for what and which is best for whom.
As a result, we are comparing Rigid PCB vs. Rigid Flex PCB vs. Flex PCB today to help you understand which PCB is which and for what purpose they are built and used.
Describe Rigid PCB
Rigid PCBs are solid, inflexible circuit boards that cannot be twisted or bent. They are made up of several layers that are bonded together with glue and heat, including a substrate layer, a copper layer, a solder mask layer, and a silkscreen layer.
Rigid PCBs can be single-sided, double-sided, or multi-layered, depending on the needs. They cannot, however, be amended or changed once made.
Why Should You Use Rigid PCB?
Rigid PCBs are an excellent choice if you need something that is inexpensive and can be produced in large quantities. They are also more robust than other boards, so if you need a long-lasting circuit board, a rigid PCB with significant circuit density is an excellent choice.
Rigid boards, which can withstand both heat and high levels of stress, are very popular in goods and industries where components must remain attached.
Application of Rigid PCB
Rigid PCBs can be found in a wide range of everyday items on which we rely for work and communication. They are also used in critical medical equipment, primarily in large, non-portable devices.
Furthermore, because of their aluminum substrates, PCBs can withstand high temperatures, making them ideal for the aerospace industry, where they are used in a variety of critical equipment.
How to Explain Flex PCB
A flexible printed circuit board or Flex PCB has unique features that make it particularly suitable for a variety of applications. A rigid circuit board differs from a
Fine Line FPC PCB in several ways.
A flex PCB, as opposed to a rigid design, is made of bendable materials that provide better resistance to shocks and movement. Because of their small size, they can cut package weight by up to 75%.
Why Should You Use Flex PCB?
They are much lighter than rigid PCBs and can fit into shapes that rigid designs cannot. After each year, the need for more powerful computer technology rises, and buyers from all industries seek higher performance with lighter weight. Such as
Flexible Printed Circuit 2 Meters Long.
As a result, Flex PCB is the only solution to this problem.
Flex PCB Use Case
The following are some of the most common applications for flexible PCBs.
Hearing aids, crucial sensors, and other devices employ Flex PCBs to provide excellent performance that can withstand wear and tear.
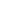
Explanation of Rigid-Flex PCB
Rigid-Flex PCBs and
Rigid-Flex PCB FR-4 Poyimide are constructed from rigid and flexible circuit boards that are tightly connected. When used correctly, rigid-flex circuit boards provide optimal solutions for difficult, limited space situations.
This technique enables the secure connection of device components while maintaining polarity and contact stability, as well as reducing plug and connector components.
Rigid-Flex circuit boards also provide dynamic and mechanical stability, allowing for 3-dimensional design flexibility, easier installation, space savings, and electrical property preservation. Rigid-Flex circuit boards can help to reduce the overall cost of the finished product.

Why Should You Use Rigid Flex PCB?
The rigid component of the circuitry on a rigid-flex printed circuit board can be directly inserted into the application. The flexible part is then twisted to fit over other parts to form another direct connection.
This feature ensures a stable connection between devices, resulting in improved performance. Laptop computers, cellphones, and smart gadgets are some of the most common items that incorporate rigid-flex PCBs into their design due to their bending characteristics.
Application of Rigid Flex PCB
A rigid-flex PCB is far more difficult to manufacture than a traditional rigid PCB. However, rigid-flex PCBs are used in designs for valid reasons, most notably when fitting the board into small spaces.
Rigid PCB vs. Rigid Flex PCB vs. Flex PCB Similarities
Although all circuit boards serve the same basic function as a platform for electrical components, the design and materials used in their manufacture distinguish them. Circuit boards are specifically designed for this purpose.
Rigid PCB vs. Flex PCB
The most obvious distinction between rigid and flex PCBs may be deduced from their names. Flex PCBs can be twisted or tailored to fit within the required system, whereas rigid PCBs are rigid. When properly constructed, flexible circuits can be bent for hundreds of thousands of cycles without failure.
Flex boards are more expensive due to their increased adaptability, but they are critical for applications with limited space, such as electronics, medical equipment, space, and automobile industries.
What distinguishes Rigid Flex from the other two?
The rigid-flex PCB, as the name suggests, is a hybrid of rigid and flex PCBs that combines the best features of both while eliminating several of their specific limitations.
A rigid-flex PCB combines flexible and rigid materials by encasing flexible circuit substrates inside rigid circuit board materials, resulting in a hybrid of flexible circuit adaptability and rigid PCB stability, strength, and circuit routing density.
This hybridization opens up a whole new world of possibilities for much more complicated and mechanically demanding designs.
Considerations When Choosing A PCB
You now understand all three types of PCBs, as well as their similarities and differences. The last topic we'd like to cover is the factors to consider when selecting a PCB.
The following are the most important factors to consider when selecting the correct PCB every time:
Durability
Because of the reduced weight of the board, we believe Flex circuits are the most durable PCB for durability.
They reduce the risk of shock damage. Because flexible PCBs are made of polyimide, they are also resistant to high temperatures. If your product must twist without breaking, both literally and metaphorically, Flex PCB is the way to go.
Cost
Flex PCBs can be extremely beneficial, but your budget may not always allow for them. While calculating your budget, consider whether flexible PCB expenses are worthwhile, and then make a decision.
Rigid PCBs are generally less expensive than flexible circuits. So, if size isn't an issue for you and you want to get the most bang for your buck, we think rigid PCBs are a good choice.
Quality
At the end of the day, the debate returns to the same point it began: which of the three PCBs comparison stands to provide you with the best quality?
We call it the hybrid Rigid-Flex PCB because it combines the best of both worlds. So, if cost, durability, and other factors aren't a big deal for you and you're just looking for the best all-arounder, we think Rigid-Flex PCB is the way to go.
Choosing a PCB can be difficult because they all have advantages and disadvantages. As a result, we have compared all three in this article to make it easier for you to decide which works best for you and why.
However, one thing you should be certain of is that, regardless of the type, if you are looking for the best PCB manufacturer in the world, Hemeixin is the place to be. To place an order, go to their website right now.
 Call Us Now !
Tel : +86 755 27374946
Call Us Now !
Tel : +86 755 27374946
 Order Online Now !
Email : info@bichengpcb.com
Order Online Now !
Email : info@bichengpcb.com