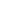
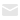
Today, a wide range of portable wireless and commerce sectors, including health, communication, etc., have adopted Microwave PCB technologies. Circuit interferences and radiation in the PCB design are difficult to control because microwave circuit boards are distributed variable circuits that continue to produce skin effects and interaction effects. The most common issues include resonance issues caused by absurd layouts, cross-interference between digital and analog circuitry, power interference with noise, and related resonance issues. As a result, it is crucial for Microwave PCB design to weigh the advantages and disadvantages of PCB design and make an effort to cut down on interference.
What is the Microwave PCB?
The RF and microwave PCB boards are distinctive and cutting-edge PCB kinds created to operate at signal frequencies between megahertz and gigahertz (medium frequency to extremely high frequency). From cellphones to military radars for network transmissions, these frequencies are used everywhere. Extremely specific materials and technology are required for this PCB equipment, which are not readily available from many producers.
How do RF and Microwave PCB differ?
The radiofrequency of RF circuit boards and microwave PCBs is their primary differentiator. Microwave PCBs are categorized as RF circuit boards that operate over 2GHz.
Microwave PCBs and RF circuit boards are used for networking signals in any application that calls for the reception and transmission of radio signals. Radar stations and mobile phones, for instance, are two common applications.
Microwave PCB advantages:
Since electronics are so useful, this technology is becoming more and more popular every day. The PCB design for microwaves has several benefits. Let's look at them now.
High Stability:
Extreme temperature PCB design is especially stable. When analog applications are used, these PCBs are capable of operating at 40 GHz.
High Speed:
Signals can pass through the PCB more quickly and imperturbably thanks to the low tangent and consistency of the loss.
Components:
Fine pitch components can be successfully mounted on the board without too many issues.
Costs reduced:
In order to reduce PCB assembly costs while maintaining optimal PCB performance, the materials may be combined in a panel storage system.
Multifaceted:
A PCB engineer can quickly align several layers of boards into complex patterns because to the usage of low CTE components.
Microwave PCB Materials:
Conductivity constant (DK), overindulgence feature, thermal expansion coefficient (CTE), dielectric constants, and current conductivity are important factors that determine laminate circuit performance for microwave/RF printed circuit boards when designing PCB components at higher frequencies.
The most identifiable different frequencies material for PCB cover workers is polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). It is a manufactured thermoplastic fluoropolymer with good radio wave dielectric properties. Here is a brief summary of the main material vendors with whom we have experience. Since all materials are handled in reverse, it is crucial to understand precisely how the components will respond to all procedures.
Since they have been producing PCBs with those materials for many years, many companies have a sizable supply of all HF laminates. These PCB applications include the RF antenna, Wi-Fi, IP backbone, optical switches, diplexers/multiplexors, signal processing, and many others.
It is essential to invest in equipment for the proper processing of these microwave PCBs as well as to have sufficient knowledge in the creation of PCBs from these products. The PCBs made from these components are essential.
1. Materials from Rogers:
As one of the oldest major public firms in the world, Rogers provides a multitude of creative and team-based methods for resolving issues with customers. In 1949, Rogers developed the first RT/duroid® material for use in electrical appliances. Today, RT/duroid® dominates the market for high-speed microwave PCBs in the PTFE family. The motto of the Rogers Organization is "Helping Our World, Protecting and Connecting Our Planet." The group combines an extensive array of solutions from any PCB maker employing high-end Rogers products with the application expertise, global resources, and engineering and design capabilities of Epic.
Since many substances differ when PCBs are handled, the majority of
PTFE PCB laminates require specialized materials and processes in order to make PCBs with the best accuracy and material capabilities. The most well-known brand name for formulations made with PTFE is Teflon.
It is used in contemporary non-stick cookware, therefore if you don't have the necessary skills, handling this substance could be challenging.
2. Panasonic MEGTRON 6
The Panasonic MEGTRON 6 is an advanced laminate circuit board technology for induction motors used in grid equipment, data centers, IC testing systems, and high-frequency measuring equipment. MEGTRON 6 is renowned for its low dielectric dissipation, low dielectric factors, low transmission loss, and high thermal expansion.
3. High-performance material from Isola:
Since 1912, Isola has led the way in the research and production of copper laminate solutions for the creation of cutting-edge, multifaceted circuit boards (PCBs). They can select basic materials with the best possible balance of cost and effectiveness. When choosing a higher RF or microwave laminate, millimeter-wave and microwave designers must take into account important factors as material thickness, dielectric constant factor, dissipation factor, and high quantity tolerance. Extremely precise stable dielectric, layer thickness, and dielectric thickness management are required for microwave high-frequency circuits. The common laminates used in Isola are listed in the table below.
4. Arlon Electronic Microwave PCB Materials:
Rogers Corporation recently bought Arlon Electronic Resources, a company that specialized in the acrylate resin process and produced polyimide, extraordinary-TG, and inexpensive thermoset laminate architectures. These resin substitutes are created on a variety of substrates, including fabric crystal and non-plaited aramid, which are used for microwave PCB trails that operate at high speeds and with reliability. Arlon supplies are frequently the best option for applications that are highly exposed to high heat, such as RF antennas, down-holes, and airplane instruments.
5. PA Materials:
Given that they can manage significantly higher power values than LNAs, the materials used in RF/microwave PA circuits have a slightly different set of critical requirements.
Similar to circuit components for LNAs, tight Dk and susceptibility control are important considerations for materials analyzed for PA circuits. These types of amplifiers produce more heat than other amplifier types, hence thermal conductivity is particularly important for PA designs. In actuality, the critical PA PCB material parameters, including as heat capacity, TCDk, and thermal expansion coefficient, are thermally related (CTE).
7. Taconic Microwave Materials:
Taconic has become a global superpower in PTFE products since 1961. With PTFE and silicone-covered materials, tapes, and panels, they offer a variety of best applications today. Low DK CTE PTFE laminates are the main focus for Taconic equipment used in RF/microwave PCB manufacture. Many Taconic devices are designed to provide world-class loss-insertion capabilities while maintaining an ultra-low fiberglass percentage and a uniform refractive index across the cover.
During the enclose, the homogeneous ceramic dispersion produces extremely low thermal expansion X or Y constants. Taconic provides materials and a list of its offerings for each use.
8. Metal Material for Microwave PCB:
Copper, aluminum, iron, and other common materials are still used in PCBs. These materials allow for the use of Surface Mount Technology (SMT) for perceptions. Mechanical endurance is also provided. As a result, the metal base PCBs have a much longer lifetime.
The various materials used in the development and installation of PCBs all have advantages and disadvantages. The material is chosen with the application, the desired outcome, environmental considerations, and any other constraints in mind. You should select the PCB material based on the expected results.
9. FR-4 Material:
This is the most common material used in PCBs. It is a laminate epoxy reinforced in glass. The epoxy is flammable and waterproof in most cases. It has a significant amount of weight strength. The tensile strength of this material is extremely high.
10. PTFE (Teflon) for Microwave PCB:
PTFE is a polymeric substance that provides no resistance and is thus used in high-speed, high-frequency applications. Because PTFE is very flexible, it is useful in low-tolerance applications. It is also very light and can be used in a variety of industries. It is also flame-resistant, has a high physical prowess, provides temperature stability, and has a wide range of applications.
 Call Us Now !
Tel : +86 755 27374946
Call Us Now !
Tel : +86 755 27374946
 Order Online Now !
Email : info@bichengpcb.com
Order Online Now !
Email : info@bichengpcb.com