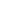
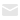
Basic Knowledge of FPC Flexible Circuit Board
With the continuous increase of the production ratio of flexible PCB and the application and promotion of rigid flexible PCB, it is now more common to add flexible, rigid or rigid flexible PCB to say how many layers of FPC it is. Generally, FPC made of soft insulating material is called soft FPC or flexible FPC, rigid flexible compound PCB called rigid flexible PCB. It is suitable for today's electronic products to high density and high reliability, small scale, lightweight direction of development needs, but also satisfied with strict economic requirements and market and technical competition needs.
Overseas, flexible PCB has been widely used in the early 1960s. In our country, only in the sixties began to produce application. In recent years, with the world economic integration and open city and introduction of technology to enhance the use quantity to constantly improve, a little small and medium-sized rigid FPC factory on this chance see fit and use soft hard work skill, use the existing facilities of tooling and process improvement, transformation yield and is suitable for flexible PCB dosage increased demand. In order to further realize PCB, this paper makes a research and discussion on flexible PCB process.
I. Classification of flexible PCB and its advantages and disadvantages
1. Flexible PCB classification
Flexible PCBS are generally classified according to the layer and structure of the conductor as follows:
1.1 Single-sided flexible PCB
A single-sided flexible PCB, with only one conductor, may have a covering layer or no covering layer. The insulation base material used varies with the application of the product. Commonly used insulating materials are polyester, polyimide, polytetrafluoroethylene, soft epoxy gas - glass cloth.
Single-sided flexible PCBS can be further classified into the following four categories:
1) Single-sided cosignation without covering layer
The wire pattern of this kind of flexible PCB is on the insulating substrate, and there is no covering layer on the outer surface of the wire. Just like the general one-sided rigid FPC. This kind of product is the cheapest kind, be used commonly in blame crucial and what setting tries to take care of should use close. The interconnection is successfully achieved by tin welding, fusion welding or pressure welding. It was often used in early telephones.
FPC flexible circuit board
2) single-sided cosignation with covering layer
This type is similar to the previous type, but according to customer requirements on the outer surface of the wire with a covering layer. Cover the pad to expose, simple can be in the end of the area is not covered. Requirements of precision can be considered appropriate and the use of clearance holes. It is one of the most widely used single-sided flexible PCB, which is widely used in transportation instrument and electronic spectrograph.
3) No covering layer signed on both sides
This type of interlocking plate interface can be interlocked on both the front and back of the wire. To do this, a path hole is made in the insulating substrate at the pad. This path hole may be made by punching, decompressing or other mechanical means at the desired position of the insulating substrate. It is used for both sides of the installation element, parts and the need for tin welding occasions, access at the pad area without insulating substrate, such pad area is generally removed by chemical methods.
Double sided flexible PCB
4) With cover layer signed on both sides
This kind is different from the previous kind is the appearance of a layer of cover layer. However, the covering layer has access holes, which allow both sides to be connected, and still maintain the covering layer. These flexible PCBS are made of two layers of insulating material and a metal conductor. Is used in the need of covering layer and surrounding devices are insulated from each other, and themselves to be insulated from each other, and the end of the need for positive and negative are co-signed occasions.
1.2 Double-sided flexible PCB
Double-sided flexible PCB with two layers of conductors. The applications and advantages of this kind of double-sided flexible PCB are the same as single-sided flexible PCB, the main advantage is to increase the density of wiring per unit plane or object surface size. It can be divided into: a without metallized hole, without covering layer and without metallized hole; B without metallized holes and with covering layer; C having metallized holes and no covering layer; D having metallized holes and covering layers. Double-sided flexible PCBS with no covering layer are rarely used.
1.3 layer flexible PCB
Flexible multilayer PCB such as rigid multilayer PCB, as appropriate and the use of multilayer compression technology, can be made of multilayer FPC flexible circuit board. The simplest multi-layer soft PCB is a three-layer flexible PCB with two copper shielding layers on both sides of a single PCB. This three-layer soft PCB is better than coaxial or shielded conductors in electrical special properties. The most commonly used multi-layer flexible PCB structure is the four-layer structure, with metallized holes successfully interconnecting layers, and the middle layer is usually the power layer and the ground layer.
The advantage of multilayer soft PCBS is that the substrate film is light in weight and has good electrical properties such as low dielectric constant. Multilayer flexible PCB made of polyimide film is about 1/3 lighter than rigid epoxy gasglass multilayer PCB, but it misses the good flexibility of single-sided and double-sided flexible PCB, which is not required for most such products.
Multi-layer flexible PCBS can be further divided into the following types:
1) The flexible insulating substrate is composed of multi-layer PCB, and the finished product is specified to be flexible: this structure is generally the two ends of many single-sided or double-sided microstrip flexible PCB are bonded together, but the inner part of the core is not bonded together, so it has a high degree of flexibility. For each line layer of a multilayer soft PCB, the signal line must be preset on the ground surface in order to have the desired electrical specific properties, such as the specific impedance performance and the rigid PCB it interconnects. To achieve a high degree of flexibility, a thin, adaptive coating, such as polyimide, may be applied over the conductor layer in place of a thicker laminated covering layer. The metallized holes enable plane Z between the flexible line layers to successfully achieve the required interconnections. This multi-layer flexible PCB is most suitable for use in presets requiring flexibility, high reliability and high density.
2) A multi-layer PCB is formed on a soft insulating base material, and the finished product can be bent: this kind of multi-layer soft PCB is made of soft insulating material, such as polyimide film, and the layer is reduced to a multi-layer board. The inherent flexibility is missed after lamination. This type of soft PCB is considered appropriate when the preset requirement is to take maximum advantage of the special properties of the film's insulation, such as low dielectric constant, average thickness medium, light weight, and ability to repeat processing. For example, multilayer PCBS made of polyimide film insulation are about one-third lighter than rigid PCBS made of epoxy gasglass cloth.
3) A multi-layer PCB is formed on a flexible insulating base material, and the finished product must be formable, rather than able to be repeated and flexed: this kind of multi-layer soft PCB is made of flexible insulating material. Although it is made of soft materials, it is already formed by the time the finished product is used because of predetermined electrical limitations, such as the requirement of a thick conductor for the desired conductor resistance, or the requirement of a thick insulation between the signal layer and the ground layer for the desired impedance or capacitance. The term "formable" is defined as a multilayer flexible PCB device that has experience in making the desired pattern and is no longer flexed during application. Application in wiring inside avionics facility units. In this case, the conductor with low resistance, minimal capacitive coupling or circuit noise, and flat and smooth buckling to 90° at the interconnect end is required. Multilayer flexible PCB made of polyimide film material successfully achieves this kind of wiring job. Because polyimide film is resistant to high temperature, flexible, and overall electrical and mechanical special properties are satisfactory. In order to achieve complete interconnection of the device profile successfully, the inner wiring area can be further divided into multiple layers of flexible circuit devices and pieced together with adhesive tape to form a printed circuit bundle.
1.4 Rigid-flexible multi-layer PCB
This type is usually on one or two rigid PCBS containing the soft PCBS necessary to form the colony. Flexible PCB layers are laminated inside rigid multilayer PCBS for special electrical requirements or to extend out of rigid circuits, which are experienced in the simplest surface circuit assembly of dynasty Z. This type of product is widely used in electronic facilities where compression weight and size are the key and high reliability, high density assembly and good electrical special properties are guaranteed.
Rigid-flexible multi-layer PCB can also put a lot of single-sided or double-sided flexible PCB end bonding suppressed together into a rigid part, and mid-waist non-bonding into a soft part, rigid part of the Z surface with metallized hole interconnection. Flexible lines can be laminated into a rigid multilayer plate. This type of PCB is increasingly used in some of the requirements of ultra-high packaging density, good electrical special properties, high reliability and strict limit size occasions.
There is already a range of hybrid multilayer flexible PCB devices preset for military avionics applications where weight and size are critical. In order to meet the specified weight and size limits, the inner packing density must be extremely high. In addition to high circuit density, in order to minimize crosstalk and noise, all signal transmission lines must be shielded. If shielded clutch wires are used, it is not economically possible to package them into the system. In this way, mixed layers are used
Flexible PCB to successfully achieve its interconnect. This device contains the shielded signal line in the flat ribbon line flexible PCB, which is then an integral part of the rigid PCB. At higher levels of operation, the PCB forms a 90° S-shaped buckling after fabrication, thus providing the simplest path for surface interconnections for Z, and the stress-strain reduction at solder joints for x, Y, and Z with the simplest surface oscillating stresses.
Flexible FPC
2. Advantages Rigid area range rigid area range
2.1 can be flexible
A significant advantage of using flexible FPC is that it can be more easily routed and connected in three dimensions, and can also be rolled or folded up for use. As long as it is curled within the allowable radius of curvature, it can withstand thousands to tens of thousands of applications without being destroyed.
2.2 Reducing the size
In the assembly and connection of components, compared with the use of wire cable, the conductor profile of flexible PCB is thin and flat, reducing the size of wire, and can be formed along the casing, so that the structure of the facility is closer and more reasonable, reducing the size of the assembly. Compared with rigid PCB, the space can be saved by 60~90 %.
2.3 Weight reduction
In the same size, the weight of the flexible PCB can be reduced by about 70 percent compared with the wire and cable at the same load, and about 90 percent compared with the rigid PCB.
2.4 Complete sameness of installation
With flexible PCB connection, eliminate the error of wire and cable connection. As long as the processing drawings have been corrected, all the winding circuits produced in the future are the same. There will be no misconnection when installing cosigned lines.
2.5 increased reliability
When it is considered appropriate to use soft PCB assembly connection, because it can be wired on the three simplest surfaces of X, Y and Z, the transfer interconnection is reduced, so that the reliability of the whole system is increased, and the fault detection is provided with convenience.
2.6 Preset controllability of electrical parameters
When implementing flexible PCB presets, presetters can control capacitance, inductance, special impedance, delay and attenuation, etc. Can be preset to have the special properties of a transmission line. Since these parameters are related to conductor width, thickness, spacing, thickness of insulation layer, dielectric constant, tangent of loss Angle, etc., it is not easy to do when it is considered appropriate to use conductor and cable.
2.7 The end can be mass solder
Like rigid PCB, soft PCB has a terminal pad to eliminate wire stripping and tin lining, thus saving cost. Terminal pads are connected to elements, parts and plugs, and can be immersed or wave welded to replace manual soldering of each wire.
2.8 Materials can be selected
Soft PCB can be made of different substrate materials according to different application requirements. For example, polyester film can be used in assembly applications requiring low cost. In demanding applications, which require good performance, polyimide films can be used.
2.9 low cost
With flexible PCB connection, the total cost can be reduced. This is due to:
1) Because of the exact uniformity of various parameters of the conductor of flexible PCB; The implementation of group termination eliminates the incorrect and overwork of cable wool mounting and connection, and the modification of soft PCB is relatively convenient.
2) The application of flexible PCB simplifies the structure preset, it can be directly pasted to the member, reducing the damage of the line clip and its fixator.
3) For shielded wires, the price of flexible PCB is lower.
2.10 Continuity of processing
Because the flexible cladding foil can be supplied in roll form, because this can successfully achieve the continuous production of FPC. This also helps to reduce costs.
3. The lack of
3.1 One-time high initial cost
Because flexible PCBS are preset and fabricated for specific applications, the cost of starting circuit presets, wiring, and photographic film is high. Unless there is a special need to apply soft PCB, generally small amount of application, it is best not considered appropriate and use.
3.2 It is difficult to change and patch flexible PCB
Once the flexible PCB is made, it must be changed from the background or woven light drawing procedure, because this is not easy to change. Its appearance cover a layer of try to take care of the film, before the repair to remove, repair after recovery, this is a difficult office.
3.3 The size is limited
Flexible PCB is generally made by intermittent process under the condition of not being popular, because it is limited by the size of production facilities and can not be made very long and wide.
3.4 Improper operation and easy to damage
The damage of the flexible circuit is easy to be induced by the improper operation of the person holding the position of installation, and the soldering and reworking need to be operated by the person holding the position of training.
 Call Us Now !
Tel : +86 755 27374946
Call Us Now !
Tel : +86 755 27374946
 Order Online Now !
Email : info@bichengpcb.com
Order Online Now !
Email : info@bichengpcb.com