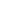
PCB in 2024 or Will Resume Growth
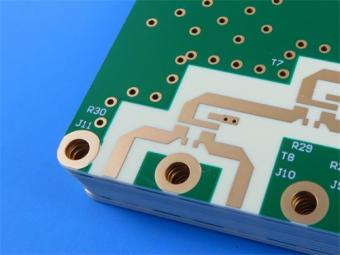
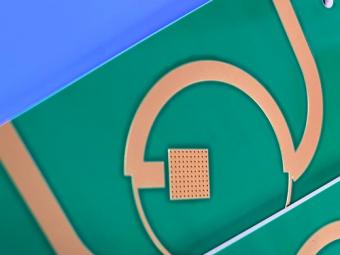
PCB in 2024 or Will Resume Growth According to analyst Zhang Yuansong from the Industrial Technology Research Institute (ITRI), the PCB industry is expected to resume growth in 2024. While the strength of the third-quarter peak season is still uncertain, the continuous destocking of consumer products and the ongoing momentum in the EV, AI server, and satellite communication sectors are expected to drive PCB output, with a potential rebound in 2024. ABF substrates will benefit from the expansion of advanced packaging, and the supply-demand gap is expected to widen in the next two years. Zhang Yuansong attended an IEK expert symposium organized by Yuanta Securities on August 28th. He believes that the automotive industry will be the only PCB terminal application with a year-on-year growth this year, especially with electric vehicles accounting for 14% to 15% of the overall automotive market. The increasing adoption of EVs will drive the demand and area of PCBs. If they can penetrate the supply chain of companies like Tesla and BYD, there will be a noticeable increase in orders in the next one to two years. Although multilayer boards accounted for 60% of the overall automotive PCB production value in the first half of this year, the increasing electrification and widespread adoption of ADAS will drive the application of HDI PCB boards in automotive radar and camera module systems. HDI and flexible boards will become the most promising segments in the automotive PCB market. Supply chain companies such as Kinwong, Unimicron, Dingying, and Jingpeng are expected to benefit from this trend. In the short term, Zhang Yuansong believes that the third quarter will see a peak season effect due to the launch of new Apple products. However, with the situation of high inflation and the recovery of mainland China not meeting expectations, the strength of the peak season remains to be observed. In 2022, the PCB industry achieved high growth, creating a higher base year for comparison. Therefore, the overall PCB output is expected to decline by 16.8% in 2023, reaching NT$769.3 billion. In 2024, driven by the synchronous recovery of mobile phones, laptops, and semiconductors, as well as the continued momentum in EVs, AI servers, and satellite communication, the overall PCB output is expected to return to growth, with an estimated annual growth rate of 8.1%. In particular, for ABF substrates, in order to meet the demand for advanced computing, chiplet heterogeneous integration packaging technology is the future trend. It can integrate chips from different fabs, different process nodes, and different properties into a single chip. This will drive the increase in the number of layers, area, and circuit density of ABF substrates, raising the manufacturing threshold. The demand for ABF substrates will be driven by advanced packaging spreading to various fields. From a situation of oversupply of 5% this year, it is expected t...
 Call Us Now !
Tel : +86 755 27374946
Call Us Now !
Tel : +86 755 27374946
 Order Online Now !
Email : info@bichengpcb.com
Order Online Now !
Email : info@bichengpcb.com