HuaTong Optimistic About the Prospects of AI, Automotive Electronics, and Satellite Boards
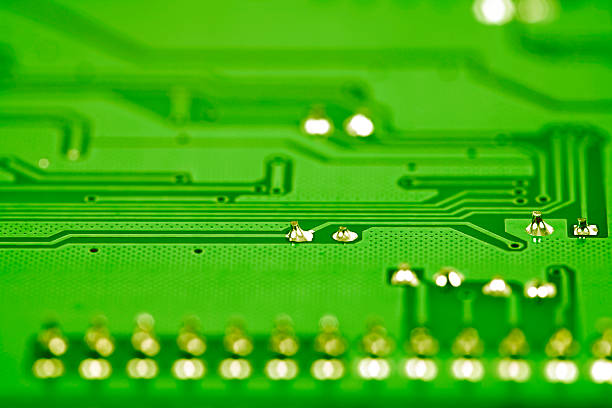
HuaTong Optimistic About the Prospects of AI, Automotive Electronics, and Satellite Boards HuaTong's Commitment to Innovation and Quality: HuaTong, one of the world's largest PCB manufacturers, continues to lead the industry with a strong focus on AI, automotive electronics, and satellite boards. This dedication to innovation and quality has positioned the company as a leader in the PCB industry. Recently, Bicheng PCB, a leading PCB supplier, shipped a new batch of high-quality PCBs made with Shengyi Tg150 ℃ S1000H material and an advanced stackup, ensuring optimal performance and durability. Bicheng PCB's Latest Shipment Features Advanced Technology and Materials: The PCBs feature a multilayer construction with blind vias on layers 1-4, with a finished board thickness of 1.6 mm. The finished copper weight is 1.0 oz (1.4 mils) all layers, and the via plating thickness is 1 mil. The surface finish is electroless nickel and immersion gold (ENIG), with top and bottom silkscreens in white and top and bottom solder masks in green. The PCBs also underwent 100% electrical testing, ensuring optimal functionality. Bicheng PCB's use of the latest technologies and materials underscores the growing demand for advanced PCBs and smart manufacturing solutions. The PCBs are lead-free and can operate in temperatures ranging from -40℃ to +85℃. They also feature impedance matching of 50 ohm +/- 10%, with single-end impedance on the outlayer, and 16mil, 14mil, and 7mil trace lines. The PCBs have 891 components, 973 total pads, 351 thru-hole pads, 271 top SMT pads, 351 bottom SMT pads, 152 vias, and 78 nets. HuaTong's focus on innovation and quality has positioned the company as a leader in the PCB industry. In a recent shareholders' meeting, Chairman Jiang Peikun expressed optimism about the prospects of AI, automotive electronics, and satellite boards. With the growth of these industries, there will be an increasing demand for 3rd, 4th, and even 7th order HDI PCBs, and HuaTong aims to leverage its technological leadership in the HDI industry to expand into broader markets. HuaTong's renowned HDI technology, along with mSAP carrier board technology, has further strengthened itsposition as a leader in the PCB industry. The company produces mid-to-high-end products and has observed that more and more products in the AI server and automotive electronics fields will use 3rd, 4th, and even 7th order HDI designs. Additionally, HuaTong's output of satellite boards is the world's largest, and the company plans to expand its production capacity to meet customer demand. Bicheng PCB's commitment to quality and innovation is in line with the industry's latest trends. The company's latest shipment of high-quality PCBs showcases its dedication to using the latest technologies and materials to ensure optimal performance and durability. The use of Shengyi Tg150 ℃ S1000H material and advanced stackup, along with impedance matching and 100% electrical testing, underscores Bicheng PCB...
 Call Us Now !
Tel : +86 755 27374946
Call Us Now !
Tel : +86 755 27374946
 Order Online Now !
Email : info@bichengpcb.com
Order Online Now !
Email : info@bichengpcb.com